The PhariaStudio Playground
The Playground is a workspace where you can interact with the available language models. You can input prompts in two modalities: prompt-only or raw text. This article covers the basic settings shown in the right sidebar and how to add custom settings for each model.
Access the Playground
To access the playground, follow these steps:
- Open PhariaStudio at https://pharia-studio.{ingressDomain}
- Sign in with your credentials.
- Select an existing project from the home page or create a new one:
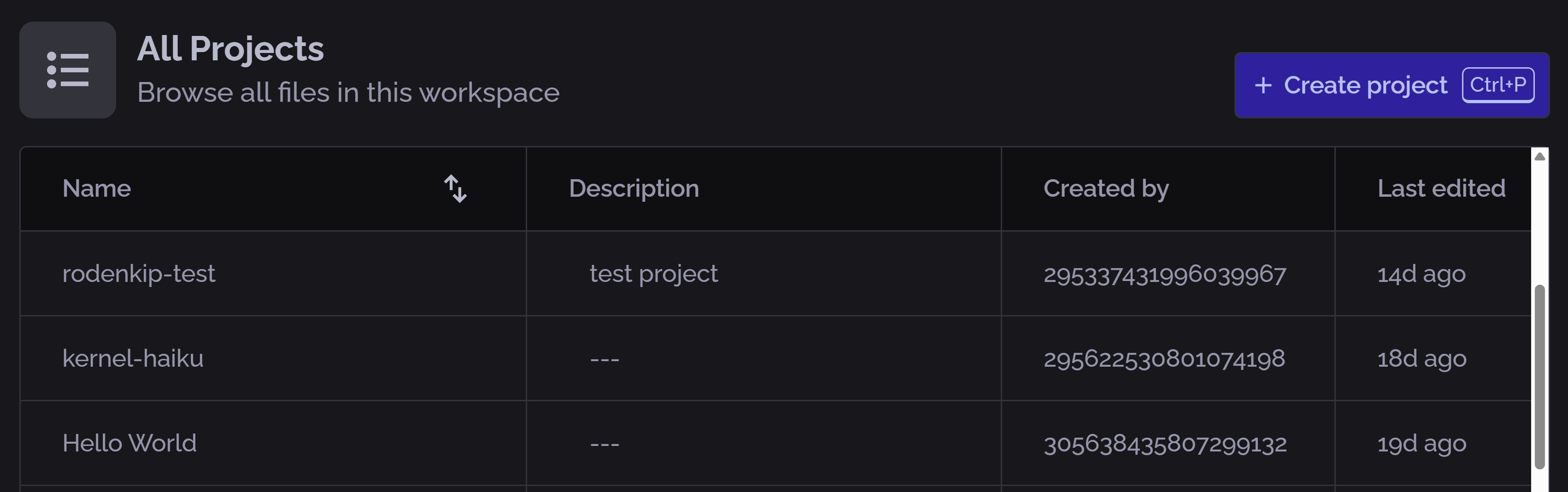
- Click Playground on the left sidebar
Select the language model
Select the desired language model from the dropdown list:
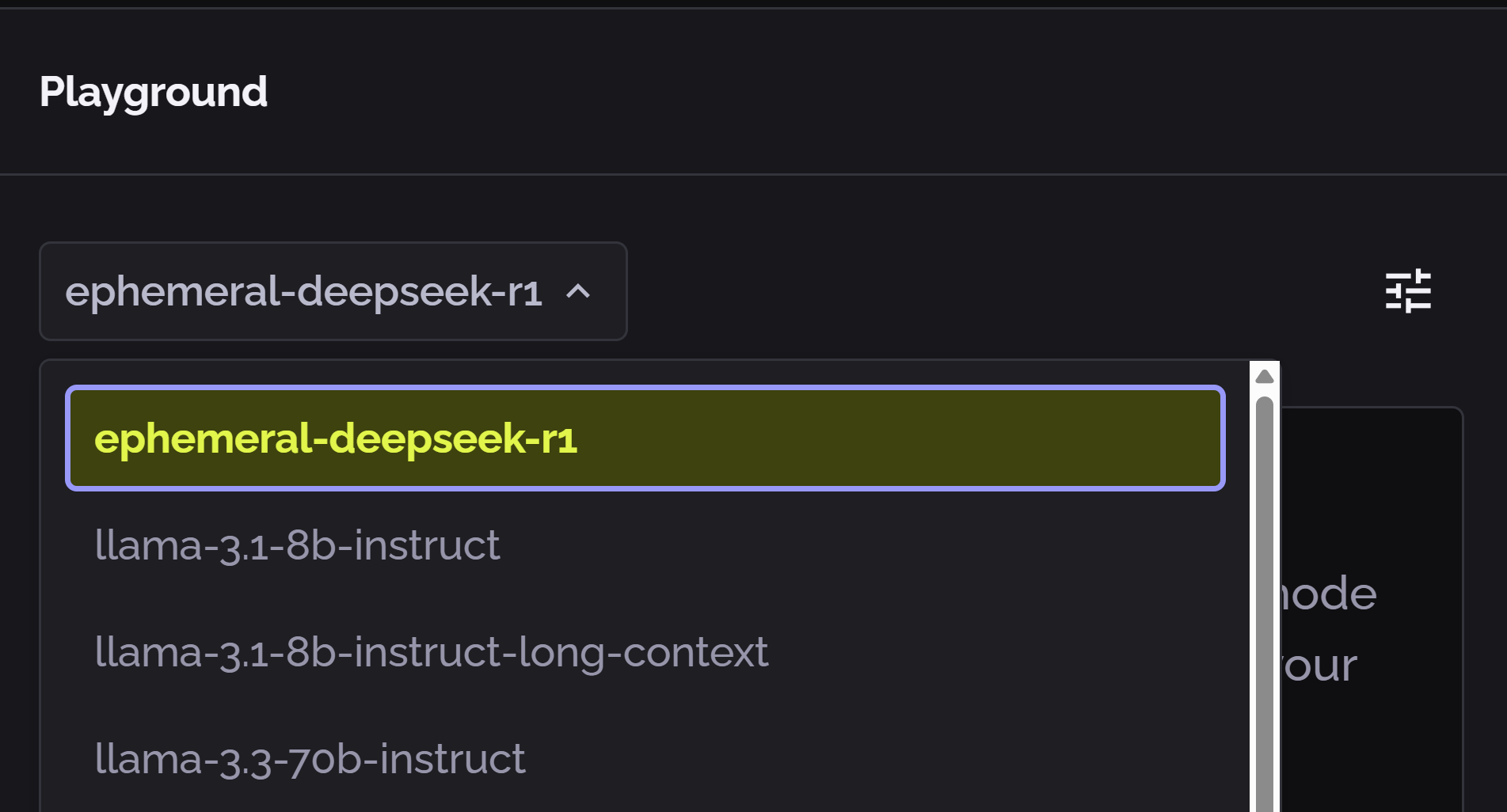
Hover your mouse near the model name to display a copy button. Click this to copy the model name to the clipboard; this is useful for entering the model name in your code.
Select the prompt input mode
Using the toggle on the bottom of the input text box, you can switch between the two modalities of prompt input:
- Only Prompt: In this mode, you focus on the pure content of the prompt, without viewing the low-level template of the model. This is suitable for single-turn interactions.
- Raw Text String: In this mode, you can change the way the prompt is sent to the model; for example, by adding a system prompt.
Each model includes its own predefined templates.
Run a prompt
- Enter text in the Prompt box.
- Click the Run button.
The content of the prompt box is sent to the language model along with any modified settings set in the Model Settings sidebar. The response is displayed in the Completion box.
Adjusting the model settings
The right sidebar contains the following basic settings:
- Maximum tokens: The maximum number of tokens allowed in the prompt.
- Temperature: A hyperparameter that controls the model's learning rate.
- Stop sequences: A list of stop words that prevent the model from processing the prompt.
- Presence penalty: A hyperparameter that penalises the model for presence of words in the prompt.
- Frequency penalty: A hyperparameter that penalises the model for frequent words in the prompt.
- Raw completion: A toggle that displays the raw completion of the model, that is, the non-optimised response.
To add custom settings for a model, follow these steps:
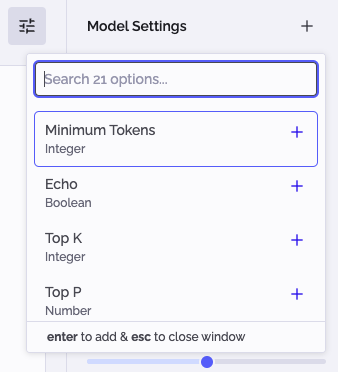
- Click the "+" button next to Model Setting in the right sidebar.
- Search and select the desired custom setting from the menu.
- Click outside the menu to return to the Playground.
- Set the desired value for the custom setting.
This allows you to add any of the supported settings for the selected model. For a complete explanation of the model settings, see the Model settings section.
Output type
By default the Playground shows the raw text output. You can render the content as Markdown by clicking Pretty at the bottom of the Completion box.
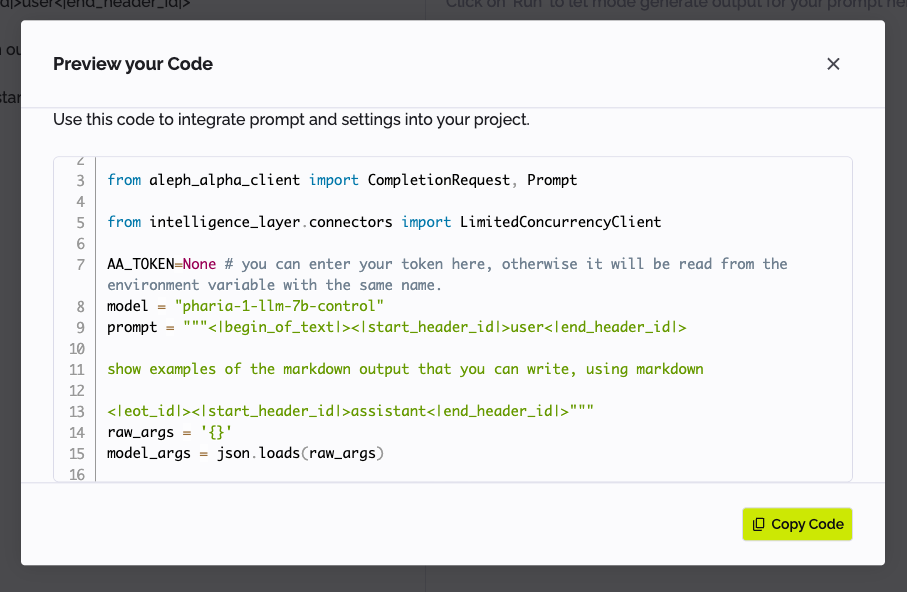
Exporting the prompt as code
Click </> Export Code at the top right of the Playground to show the code for the prompt, which you can then copy. This is helpful to speed up your development process.
Model settings
Maximum tokens (int, optional, default none)
The maximum number of tokens to be generated. Prompt completion terminates when the maximum number of tokens is reached. Increase this value to generate longer texts.
Temperature (float, optional, default 0.0)
A higher sampling temperature encourages the model to be "more creative", that is, to produce less probable outputs. Values are expected in a range from 0.0 to 1.0. You can try high values (such as 0.9) for a more "creative" response. The default 0.0 usually produces a well defined and repeatable answer.
It is recommended to use temperature or Top K or Top P (see below), but not all at the same time. If a combination of temperature, Top K or Top P is used, the rescaling of logits with temperature is performed first. Then Top K is applied. Finally, Top P is applied.
Top K (int, optional, default 0)
Top K introduces random sampling from generated tokens by randomly selecting the next token from the k most likely options. A value larger than 1 encourages the model to be more "creative". Set to 0 if you want to produce repeatable output.
It is recommended to use temperature or Top K or Top P (see below), but not all at the same time. If a combination of temperature, Top K or Top P is used, the rescaling of logits with temperature is performed first. Then Top K is applied. Finally, Top P is applied.
Top P (float, optional, default 0.0)
Top P introduces random sampling for generated tokens by randomly selecting the next token from the smallest possible set of tokens whose cumulative probability exceeds the probability Top P. Set to 0.0 if you want to produce repeatable output.
It is recommended to use temperature or Top K or Top P, but not all at the same time. If a combination of temperature, Top K or Top P is used, the rescaling of logits with temperature is performed first. Then Top K is applied. Finally, Top P is applied.
Repetition penalties include completion (bool, optional, default true)
This option determines whether the presence penalty and/or frequency penalty (see below) are updated by the generated completion text.
Repetition penalties include prompt (bool, optional, default false)
This option determines whether the presence penalty and/or frequency penalty (see below) are updated by the prompt text.
Presence penalty (float, optional, default 0.0)
The presence penalty reduces the probability of generating tokens that are already present in the generated text (Repetition penalties include completion is true) or in the prompt (Repetition penalties include prompt is true).
The presence penalty is independent of the number of occurences. Increase the value to produce text that does not repeat the input.
Frequency penalty (float, optional, default 0.0)
The frequency penalty reduces the probability of generating tokens that are already present in the generated text (Repetition penalties include completion is true) or in the prompt (Repetition penalties include prompt is true).
The frequency penalty is dependent on the number of occurences of a token. Increase the value to produce text that reduces repetition in the input.
Use multiplicative presence penalty (bool, optional, default true)
This option determines whether the presence penalty is applied multiplicatively (true) or additively (false). This changes the formula for presence and frequency penalties.
Penalty bias (string, optional)
If set, all tokens in this text are used in addition to the already penalised tokens for repetition penalties. These consist of the generated completion tokens if Repetition penalties include completion is true and the prompt tokens if Repetition penalties include prompt is true.
Penalty exceptions (List(str), optional)
You can provide a list of strings that can be generated without penalty, regardless of other penalty settings.
This option is particularly useful for a completion that uses a structured few-shot prompt.
Stop sequences (List(str), optional, default none)
You can provide a list of strings that stop generation if they are themselves generated.
Stop sequences are useful in structured texts.
Penalty exceptions include stop sequences (bool, optional, default true)
By default, stop sequences are included in the penalty exceptions. This avoids penalising the presence of stop sequences in few-shot prompts to provide structure to your completions.
Set this to false to exclude stop sequences from the penalty exceptions.
Disable optimisations (bool, optional, default false)
We continually research optimal ways to work with our models. By default, we apply these optimisations to both your prompt and completion. This helps to improve your results while using our API.
Set this option to true to keep your prompt and completion unaffected by any optimisations.
Minimum tokens (int, default 0)
Generate at least this number of tokens before an end-of-text token is generated.
Echo (bool, default false)
Include the prompt in the completion. This can be helpful when log_probs is set to return logprobs for the prompt.
Use multiplicative frequency penalty (bool, default false)
This option determines whether the frequency penalty is applied multiplicatively (true) or additively (false). This changes the formula for presence and frequency penalties.
Sequence penalty (float, default 0.0)
A higher sequence penalty reduces the probability of reproducing token sequences that already appear in the prompt (Repetition penalties include prompt is true) or previous completions (Repetition penalties include prompt is true).
Sequence penalty min length (int, default 2)
This option defines the minimal number of tokens to be considered as a sequence. The value must be two or greater.
Use multiplicative sequence penalty (bool, default false)
This option determines whether the sequence penalty is applied multiplicatively (true) or additively (false).
Completion bias inclusion (List[str], default [])
You can bias the completion results by generating only the strings that you include in this list. All other tokens are disregarded in sampling.
Note that strings in the inclusion list must not be prefixes of strings in the exclusion list, and vice versa.
Completion bias inclusion first token only (bool, default false)
This option applies the Completion bias inclusion list only to the first token.
Completion bias exclusion (List[str], default [])
You can bias the completion results by not generating the strings that you include in this list. All other tokens are unaffected in sampling.
Note that strings in the inclusion list must not be prefixes of strings in the exclusion list, and vice versa.
Completion bias exclusion first token only (bool, default false)
This option applies the Completion bias exclusion list only to the first token.
Contextual control threshold (float, default 0)
When set to zero, attention control parameters only apply to those tokens that have explicitly been set in the request. If set to a non-zero value, we apply the control parameters to similar tokens as well. Controls that have been applied to one token are applied to all other tokens that have at least the similarity score defined by this parameter. The similarity score is the cosine similarity of token embeddings.
Control log additive (bool, default true)
When set to true, control is applied by adding the log(control_factor) to the attention scores.
When set to false: control is applied by (attention_scores - - attention_scores.min(-1)) * control_factor.
Raw completion (bool, default false)
When set to true, the option forces the raw completion of the model to be returned. For some models, we may optimise the completion generated by the model and return the optimised completion in the completion field of the CompletionResponse. The raw completion, if returned, contains the non-optimised completion.